Graphical User Interface
The TASverter graphical user interface
is started by running the TASverterGUI command.
The TASverterGUI main window should then appear:
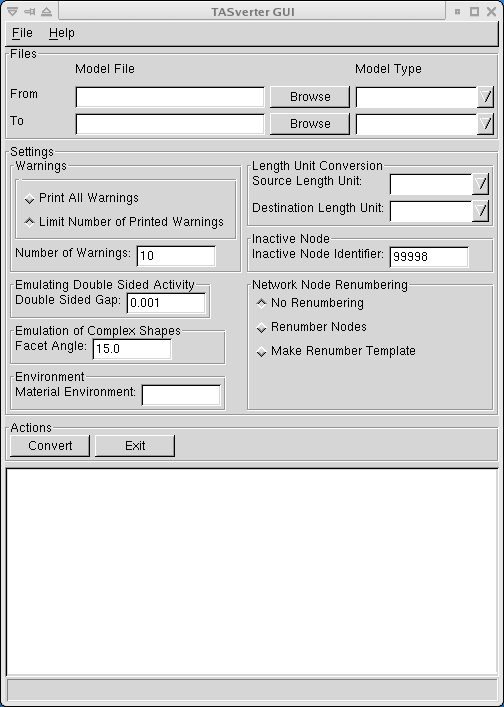
Figure 2: TASverterGUI Main Window
The TASverterGUI is a simple graphical user interface layer that calls
the main TASverter tool. The GUI provides access to the full capabilities
of TASverter in an intuitive way so that the user can easily experiment
and learn about TASverter and its options. The information that the user
enters in the TASverterGUI input fields is converted into an appropriate
TASverter command line that is then run using the appropriate underlying
operating system. The output generated by TASverter is captured and
displayed
in the text area of the TASverterGUI.
By default, the TASverterGUI expects to find TASverter located in the
same directory or folder as itself. If this is not the case, the user
must specify the correct location of TASverter using the
Preferences
dialog otherwise the execution of TASverter will fail.
The TASverterGUI consists of one main window containing all the
menus, edit boxes, buttons, etc. needed to specify the parameters and options
to be passed to TASverter. These controls are grouped
in the following way:
The Menu Bar
There are only two menus in the TASverterGUI menu bar:
The
File
menu has three options:
-
New:
instructs the TASverterGUI to reset all of the controls back to their
default values in order to start a new conversion from a consistent state.
-
Preferences:
pops up a dialog that allows the user to specify where the
TASverter script or executable is located
(see Dialogs).
-
Exit:
closes the application. The TASverterGUI can also be closed by pressing
the Exit button in the Actions group of controls.
The
Help
menu contains the following options:
-
Help:
displays this help.
-
Credits:
displays the credits for this software.
-
Copyright:
displays the copyright for this software.
-
About:
displays summary information about the TASverterGUI.
The Files input area
These controls allow the user to choose the source and destination file
names and types for the conversion to be performed by TASverter.
-
From Model File input field:
allows the user to enter the full path of the file to be converted.
-
From Browse button:
pops up a file chooser dialog so that the user can navigate the file
system to locate the file to be converted.
-
From Model Type menu button:
allows the user to choose the format of the input file to convert from
a menu of formats supported by TASverter.
-
To Model File input field:
allows the user to enter the full path of the file to which the
converted model will be written.
-
To Browse button:
pops up a file chooser dialog so that the user can navigate the file
system to specify the output file.
-
To Model Type menu button:
allows the user to choose the format of the output file from a menu
of formats supported by TASverter.
The Settings input area
These controls allow the user to specify particular options to be passed
TASverter.
-
Warnings:
correspond to the TASverter options --all_warnings
and --max_warnings_number of TASverter
-
Print All Warnings:
all warnings produced by TASverter are reported immediately to the user.
-
Limit Number of Printed Warnings:
the number of warnings of the same type that are reported immediately
to the user will be limited to the value in the "Number of Warnings"
input field.
Note that although these options affect the warnings that are reported
immediately to the user, TASverter always records all warnings in the log file.
-
Length Unit Conversion:
specify the length units to be used for the source and destination models.
These buttons correspond to the --source_length_unit
and --destination_length_unit options of TASverter.
-
Source Length Unit:
specify the length units used in the source model.
If no unit is specified in the source model itself, the source length
unit defaults to "metre".
-
Destination Length Unit:
specify the length units used in the destination model.
If no unit is specified, or used implicitly by the destination model
format, the destination length unit defaults to "metre".
These menu buttons allow the user to choose one of the supported length
units. The accepted units are:
m (metre), cm (centimetre), mm (millimetre), in (inch) and ft (foot).
-
Emulating Double Side Activity:
set the value for the --double_sided_gap parameter that may be
passed to TASverter.
This option is useful as a work around solution for those analysis tools
which do not allow different thermal node numbers for the two sides of a
double-sided surface where both surfaces are active. For those particular
tools, TASverter generates two surfaces with a single active face each
separated by the given gap size. The two separate single-sided surfaces
can then have different thermal node numbers.
See also
Different nodes on both sides of same surface
in the section on Thermica Geometry conversion.
-
Emulation of Complex Shapes:
set the value for the --facet_angle parameter that may be
passed to TASverter.
This option specifies the angle, in degrees, to be spanned by conical
facets when approximating complex shapes. This is used for the TRASYS
spheroid, ogive and toroid.
-
Inactive Node:
sets the value for the --inactive_node parameter that may
be passed to TASverter. The value in the input field is used as the
thermal node number to be assigned to double-sided surfaces where
both faces are inactive.
This option is useful for those analysis tools which apply a special
meaning to double-sided surfaces where both faces are inactive. Note
that the inactive side of a double-sided surface where only one face
is inactive is handled automatically by the analysis tools themselves.
-
Network Node Renumbering:
activates the --renumber and --make_renumber_template
parameters that may be passed to TASverter. By default, these options are
not activated.
-
No Renumbering:
if this option is set, TASverter does not renumber thermal nodes.
-
Make Renumber Template:
forces TASverter to generate a template for the renumbering input file.
TASverter will also generate a sorted list of thermal node numbers from
which the free node number ranges can be identified.
Note that this option may be automatically activated by TASverter when:
-
The maximum node number in the original model exceeds the supported
maximum node number allowed in the destination tool format.
In this case, the user is required to specify a renumbering such
that the maximum node number is not exceeded.
-
The original model contains a thermal network model with submodels
and the destination tool format does not support submodels. In
this case, the user is required to specify a renumbering such that
thermal nodes with the same node numbers but in different submodels
are mapped to different node numbers.
-
Renumber Nodes:
if this option is set, TASverter attempts to renumber thermal nodes
using the renumbering specified in a file called "SOURCE_FILE.renumber".
This file can be created using the Make Renumber Template option;
editing the generated file to specify the actual nodes that the user
wants to renumber; and renaming this file to "SOURCE_FILE.renumber".
-
Material Environment:
sets the value for the --material_environment parameter
that may be passed to TASverter. This option allows the selection of the
preferred material environment in the case that the source model contains
more than one material environment and the format of the destination
does not support multiple material environments.
The Action Buttons
The following actions buttons are available:
-
Convert:
calls TASverter using the values specified in the
Files and Settings
input areas described above.
The input and output files and formats must be specified.
-
Exit:
closes the TASverter GUI. This is equivalent to selecting Exit from
the File menu.
The Message Area
The Message Area displays all of the text output generated while
running TASverter from the GUI.
The TASverterGUI does not perform any further analysis of the output, so
the user must check the contents of the Message Area to determine whether
the TASverter conversion was successful.
Note that the information printed in the Message Area can also be found
in the log files generated by TASverter.
The Dialogs
The TASverterGUI uses very few dialogs and most of them only present
information to the user rather then requiring input from the user.
The current version of the TASverterGUI only
contains one dialog of this type: the Preferences Dialog.
The Preferences dialog shown below pops up when the user selects
the Preferences option from the File menu.
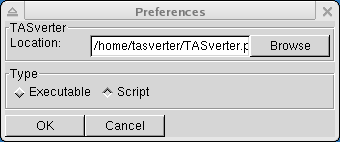
Figure 3: The Preferences Dialog
This dialog allows the user to specify where TASverter executable or script
is located.
The user must explicitly set this to the location of the TASverter executable.
The Location entry field must contain the directory and file name of
TASverter. The directory may be an absolute path from the top of the file system
or it may be relative to the location of the TASverterGUI.
The Browse button allows the user to navigate the file system and
select the TASverter executable file or script.
The Type buttons allow the user to choose between:
-
Executable:
specifies that TASverter is an executable file. This is the default.
-
Script:
specifies that TASverter is a Python script. In this
case, the user must have access to the TASverter source code and must
have access to a Python interpreter with which to run it.
Note:
These options must be set correctly for TASverter to run properly because
they affect how the TASverterGUI generates the TASverter command line
and how it is executed by the underlying operating system.


